X (formerly Twitter) Webhooks
To integrate X (formerly Twitter) webhooks with ngrok:
This guide covers how to use ngrok to integrate your localhost app with X by using Webhooks. X webhooks can be used to notify an external application whenever specific events occur in your X account.
By integrating ngrok with X, you can:
- Develop and test X webhooks locally, eliminating the time in deploying your development code to a public environment and setting it up in HTTPS.
- Inspect and troubleshoot requests from X in real-time via the inspection UI and API.
- Modify and Replay X Webhook requests with a single click and without spending time reproducing events manually in your X account.
- Secure your app with X validation provided by ngrok. Invalid requests are blocked by ngrok before reaching your app.
Step 1: Start your app
For this tutorial, we'll use the sample NodeJS app available on GitHub.
To install this sample, run the following commands in a terminal:
Loading…
This will get the project installed locally.
Now you can launch the app by running the following command:
Loading…
The app runs by default on port 3000.
You can validate that the app is up and running by visiting http://localhost:3000. The application logs request headers and body in the terminal and responds with a message in the browser.
Step 2: Launch ngrok
Once your app is running successfully on localhost, let's get it on the internet securely using ngrok!
-
If you're not an ngrok user yet, just sign up for ngrok for free.
-
Go to the ngrok dashboard and copy your Authtoken.
Tip: The ngrok agent uses the auth token to log into your account when you start a tunnel. -
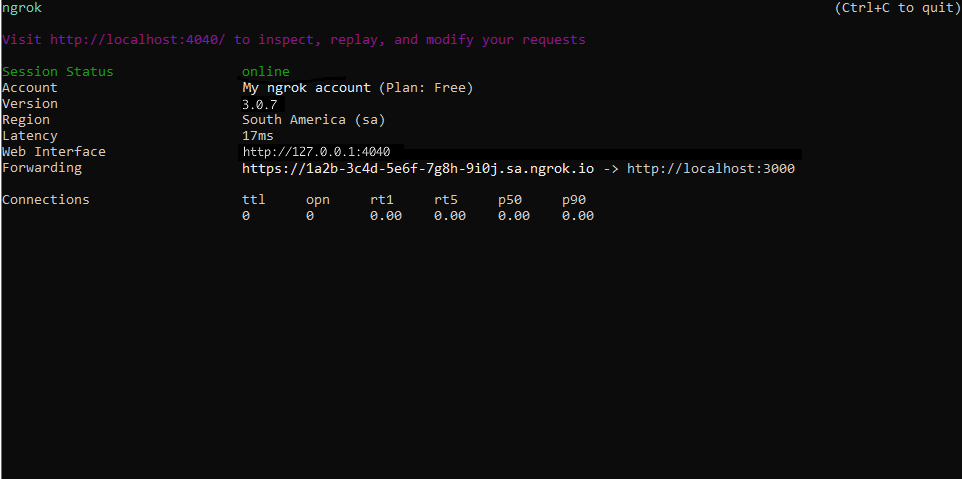
Start ngrok by running the following command:
Loading…
-
ngrok will display a URL where your localhost application is exposed to the internet (copy this URL for use with X).
Step 3: Integrate X��
To register a webhook on your X account follow the instructions below:
-
Access the X Developer Portal, sign in using your X account, and then click Developer Portal.
Tip: In order to continue, you need to have an approved developer account in the X developer portal. -
On the Dashboard page, click Create Project, enter
ngrokin the Project name field, and then click Next. -
In the Use case tab, select your role as Student and then click Next.
-
Enter
ngrok webhook docsin the Project description field and click Next. -
On the Choose an App environment page, select Development as the App environment, enter a name for your app in the App name field and then click Next.
-
On the Here are your keys & tokens page, make note of the value of the API Key, API Key Secret, and Bearer Token fields.
-
On the left menu, click Projects & Apps, click ngrok, and then click your app.
-
On the app page, click the Keys and tokens tab, click Generate in the Access Token and Secret section, and then copy the value of the Access Token and Access Token Secret fields.
-
On the left menu, click Products, click Premium, and then click Dev environments.
-
On the Dev environments page, click Set up dev environment in the Account Activity API section, enter a name for environment and then select you app in the App combobox.
-
In a terminal window, run the following command to register the webhook:
Loading…
Note: Replace the following with values copied on previous steps:
- APP_NAME: Your app name.
- ENCODED_URL: the URL provided by the ngrok agent to expose your application to the internet encoded (i.e.
https%3A%2F%2F1a2b-3c4d-5e6f-7g8h-9i0j.sa.ngrok.io). - CONSUMER_KEY: the app API Key.
- ACCESS_TOKEN: The bearer token you copied before.
-
Copy the ID of the webhook you created.
-
In a terminal window, run the following command to subscribe a user to this webhook:
Loading…
Note: Replace the following with values copied on previous steps:
- APP_NAME: Your app name.
- CONSUMER_KEY: the app API Key.
- SUBSCRIBING_USER_ACCESS_TOKEN: The access token from a X user.
Run Webhooks with X and ngrok
X sends different request body contents depending on the event that is being triggered. You can trigger new calls from X to your application by following the instructions below.
-
Acces X, sign in and post a tweet.
Confirm your localhost app receives a notification and logs both headers and body in the terminal.
Inspecting requests
When you launch the ngrok agent on your local machine, you can see two links:
- The URL to your app (it ends with
ngrok-free.appfor free accounts orngrok.appfor paid accounts when not using custom domains) - A local URL for the Web Interface (a.k.a Request Inspector).
The Request Inspector shows all the requests made through your ngrok tunnel to your localhost app. When you click on a request, you can see details of both the request and the response.
Seeing requests is an excellent way of validating the data sent to and retrieved by your app via the ngrok tunnel. That alone can save you some time dissecting and logging HTTP request and response headers, methods, bodies, and response codes within your app just to confirm you are getting what you expect.
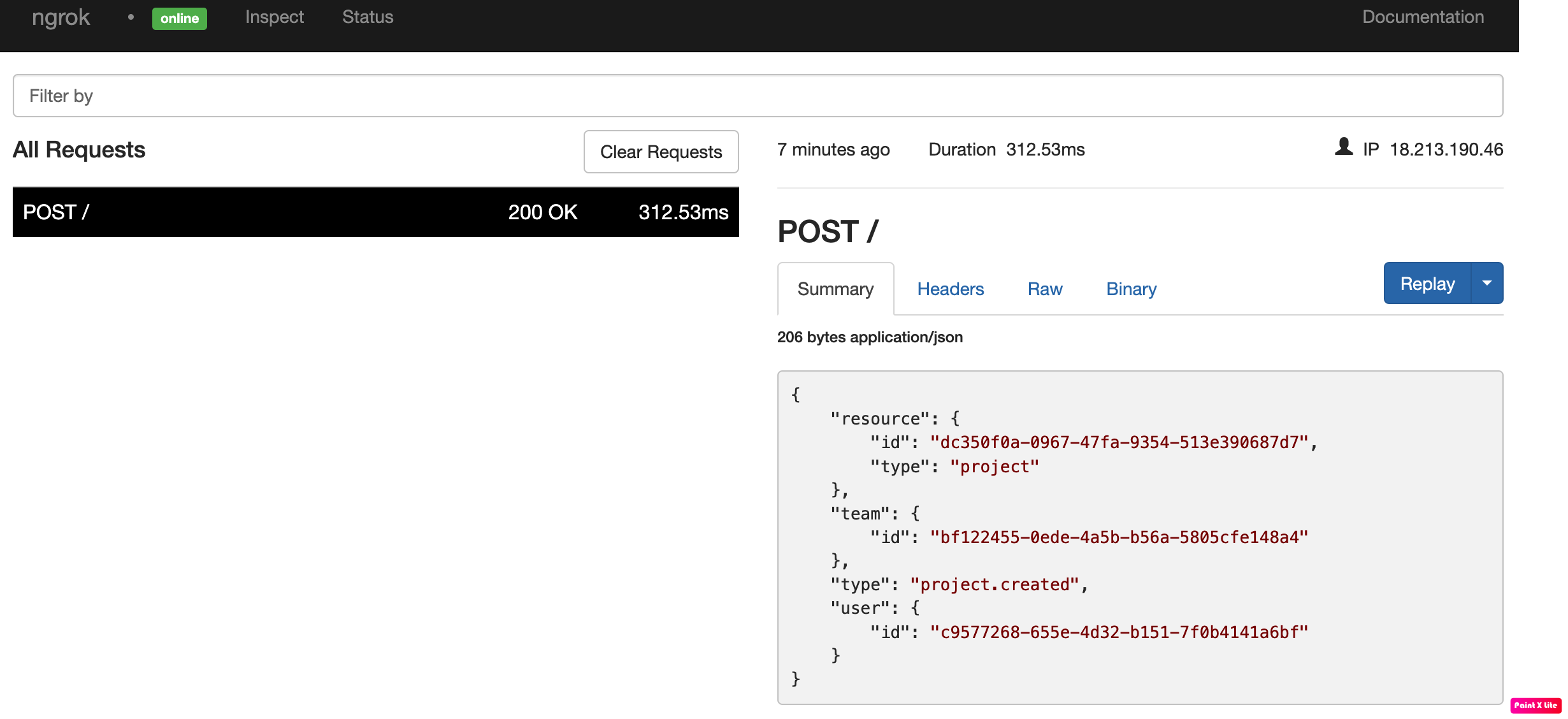
To inspect X's webhooks call, launch the ngrok web interface (i.e. http://127.0.0.1:4040), and then click one of the requests sent by X.
From the results, review the response body, header, and other details:
Replaying requests
The ngrok Request Inspector provides a replay function that you can use to test your code without the need to trigger new events from X. To replay a request:
-
In the ngrok inspection interface (i.e.
http://localhost:4040), select a request from X. -
Click Replay to execute the same request to your application or select Replay with modifications to modify the content of the original request before sending the request.
-
If you choose to Replay with modifications, you can modify any content from the original request. For example, you can modify the id field inside the body of the request.
-
Click Replay.
Verify that your local application receives the request and logs the corresponding information to the terminal.
Secure webhook requests
The ngrok signature webhook verification feature allows ngrok to assert that requests from your X webhook are the only traffic allowed to make calls to your localhost app.
Note: This ngrok feature is limited to 500 validations per month on free ngrok accounts. For unlimited, upgrade to Pro or Enterprise.
This is a quick step to add extra protection to your application.
-
During the webhook registration you provide a
-
On the top menu of the developer site, click DEVELOPER TOOLS and then click Webhooks.
-
On the Webhooks page, click Copy to copy the Secret value.
-
Restart your ngrok agent by running the command, replacing
{your webhook secret}with the value you copied before:Loading…
-
Access X and post a new tweet.
Verify that your local application receives the request and logs information to the terminal.