Ingress to services in a Consul Service Mesh on Kubernetes
To use the ngrok Kubernetes Operator with Consul in a local demo environment:
Introduction
The ngrok Kubernetes Operator is our official open-source controller for adding public and secure ingress traffic to your k8s services. It works on any cloud, local, or on-prem Kubernetes cluster to provide ingress to your services no matter the network configuration, as long as it has outbound access to the ngrok service. This allows ngrok to be portable and work seamlessly across any type of infrastructure.
Consul is a secure and resilient service mesh that provides service discovery, configuration, and segmentation functionality. Consul Connect provides service-to-service connection authorization and encryption using mutual TLS, automatically enabling TLS for all Connect services. Consul can be used with Kubernetes to provide a service mesh for your Kubernetes cluster.
Together, Consul provides a robust and secure way for Services within a cluster to communicate, while ngrok can seamlessly and securely provide public ingress to those services. This guide will walk you through setting up a Consul Service Mesh on Kubernetes and then using the ngrok Kubernetes Operator to provide ingress to your services to illustrate how they can work together.
- An ngrok account.
- kubectl
- Helm 3.0.0+
- A remote or local Kubernetes cluster with Consul installed OR minikube to set up a demo cluster locally.
Step 1: Set up a local Consul Service Mesh on Kubernetes
For this guide, we'll need access to a remote or local Kubernetes cluster with Consul installed. If you have an existing cluster with Consul set up, you can skip this step and proceed to Step 2: Install the ngrok Kubernetes Operator.
If you don't have one set up, we'll set up a local Minikube cluster and install Consul now.
- Create a local cluster with minikube
Loading…
- Create a file called
values.yamlwith the following contents:
Loading…
- Install the Consul Helm chart
Loading…
kubectl get pods --namespace consul -w- Verify Consul is installed and all its pods are healthy
Loading…
We now have a Kubernetes cluster with a Consul service mesh installed.
These steps are based on Consul's Tutorial Consul Service Discovery and Service Mesh on Minikube
Step 2: Install the ngrok Kubernetes Operator
Now that we have a Kubernetes cluster with Consul installed, we can install the ngrok Kubernetes Operator to provide ingress to our services. We'll use Helm to install the ngrok Kubernetes Operator into our cluster and use pod annotations to enable the Consul Connect sidecar injector. This will allow us to use Consul Connect to secure the traffic between the ngrok Kubernetes Operator and our services.
- First, we need to create a Kubernetes Service for the ngrok Kubernetes Operator. Consul relies on this to name our services to declare Service Intention
sourceanddestinationvalues. We'll create a Kubernetes Service for the ngrok Kubernetes Operator in theconsulnamespace.
Loading…
- Add the ngrok Kubernetes Operator Helm repo
Loading…
- Set your environment variables with your ngrok credentials. Replace
[AUTHTOKEN]and[API_KEY]with your Authtoken and API key for your account.Loading…
- Install the ngrok Kubernetes Operator
Next, we'll install the ngrok Kubernetes Operator into our cluster. We want the controller pods to be in the Consul service mesh in order to proxy traffic to our other services. We'll use pod annotations to enable the Consul Connect sidecar injector and allow outbound traffic to use the Consul mesh. Consul documents how to set these 2 annotations in the Configure Operators for Consul on Kubernetes doc.
Loading…
Loading…
- HashiCorp's docs also mention the annotation
consul.hashicorp.com/transparent-proxy-exclude-inbound-ports. This is not applicable to the ngrok Kubernetes Operator as we create an outbound connection for Ingress rather than exposing ports. - The
--set-stringflag allows the pod annotation to escape the.character in the annotation name while ensuring the valuetrueis a boolean and not a string. - In a production environment, or anywhere you wish to use Infrastructure as Code and source control your Helm configurations, you can set up your credentials following this guide.
- Verify the ngrok Kubernetes Operator is installed and all its pods are healthy
Loading…
Step 3: Install a Sample Application
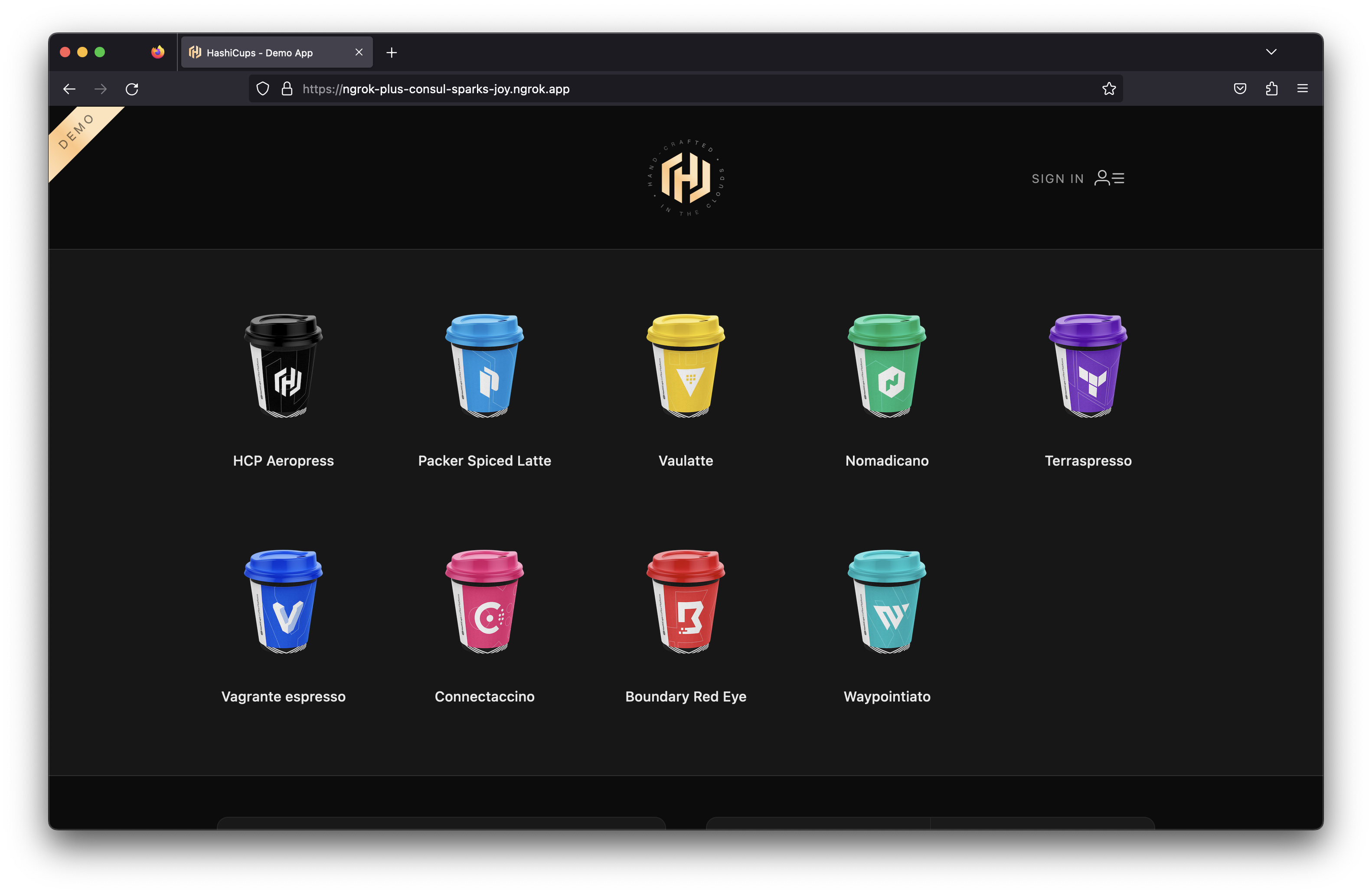
Now let's install a sample application to try out our service mesh and Operator combination. We'll use the HashiCups Demo Application HashiCorp uses for demos and guides such as in their Getting Started with Consul Service Mesh for Kubernetes guide. This application is a simple e-commerce application that allows users to order coffee cups.
The application has a frontend and public API services that are also backed by a private API and database. These communicate with each other through the Consul service mesh. This comes with nginx installed as a proxy for the frontend and Public API services. We'll replace this with ngrok to provide public access and other features.
consul namespace.The ngrok Kubernetes Operator can send traffic to services across different namespaces, but Consul Service Intentions across namespaces require an enterprise account. For now, we'll keep everything in the same namespace.
- Clone the HashiCorp Learning Consul repo. This has multiple great example applications for learning about Consul and Kubernetes. We'll use the HashiCups application for this guide.
Loading…
- Install the HashiCups sample app in the
consulnamespace. This app consists of multiple Services and Deployments that make a tiered application. We'll install all of them from this folder and then modify things from there.
Loading…
- Remove the existing Service Intentions for the
public-apiandfrontendservices and add our own.
Consul has the concept of Service Intentions. In short, they are a programmatic way to configure the Consul Service mesh to allow or deny traffic between services.
HashiCups comes with nginx installed with intentions to the frontend and public-api services. We'll remove these and add our own intentions to allow traffic from the ngrok Kubernetes Operator to the frontend and public-api services.
Loading…
- Create Service Intention from ngrok to HashiCups and the public-api
Loading…
Loading…
Step 4: Configure Public Ingress for the sample application
Now that the ngrok Kubernetes Operator can communicate with the frontend service and public-api service through the Consul Service Mesh via Service Intentions, we can create an ingress to route traffic to the app. We'll create ingress objects to route traffic to the frontend service and the public-api service.
Update the line host: $NGROK_DOMAIN_NAME in the ingress object below to your ngrok domain name. For a free account, select something unique that is a subdomain of ngrok.app. For example, host: my-unique-hashicups.ngrok.app.
Loading…
- Uses the
ngrokingress class - The host is the ngrok domain name you selected that is static
- There is a route for
/that routes to thefrontendservice on port3000 - There is a route for
/apithat routes to thepublic-apiservice on port8080
Open your $NGROK_DOMAIN_NAME domain in your browser and see the HashiCups application!
Step 5: Add OAuth Protection to the App
Now that we have the HashiCups application running, we can add OAuth protection to it. We'll use the OAuth module of the ngrok Kubernetes Operator to add OAuth protection to the app. This will allow us to use Google OAuth to protect the app.
- Create an NgrokModuleSet
The NgrokModuleSet is a custom resource that allows you to configure the modules of the ngrok Kubernetes Operator. We'll create one to configure the OAuth module. Create the following NgrokModuleSet
Loading…
This example uses the ngrok Managed OAuth Application for simplicity. To use your own Managed OAuth Application, you can try Creating a custom Google OAuth application or use an existing one.
You can then create a Kubernetes Secret with the clientId and clientSecret and reference the secret in your module set like this example.
- Add the module to the ingress
Now that we have the module set created, we can add it to the ingress. We'll add an annotation to the ingress to add the module set to it.
Loading…
This applies the OAuth module to each route on our ingress object. Navigate to your HashiCups app at $NGROK_DOMAIN_NAME and you'll see the Google OAuth screen.
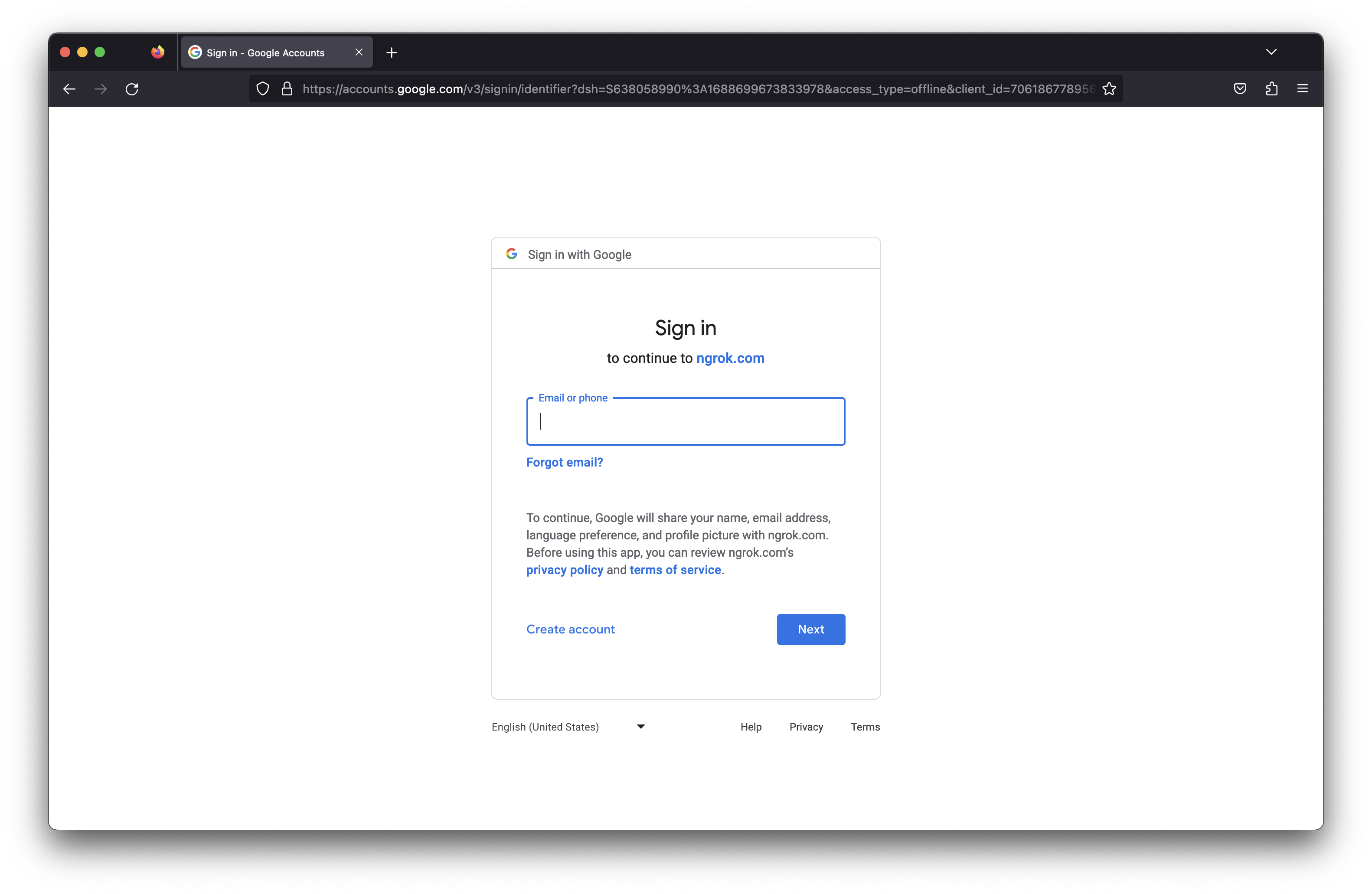
Sign into your account and you'll be redirected to the HashiCups app! Now only you can order from HashiCups from anywhere!